Material Composition:
Titanium Alloy: Orthopedic bone plates are commonly manufactured from titanium alloys, which offer a combination of high strength, low density, and excellent biocompatibility. Titanium’s biocompatibility reduces the risk of adverse reactions and facilitates bone integration.
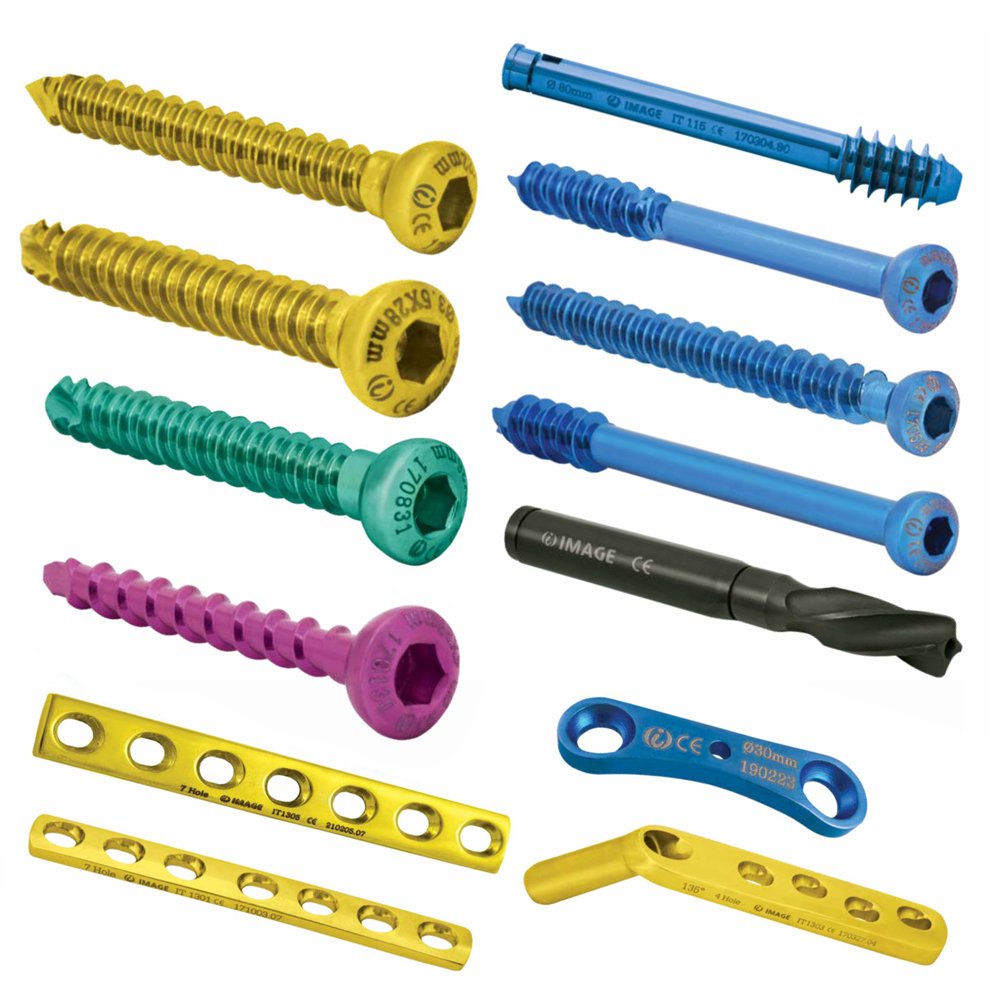
Types of Orthopedic Bone Plates:
Compression Plates: Designed to compress bone fragments together, promoting stability.
Locking Plates: Feature screws that lock into the plate, providing additional stability and facilitating a fixed-angle construct.
Dynamic Compression Plates (DCP): Allow compression at the fracture site through eccentrically placed screw holes.
Limited Contact Dynamic Compression Plates (LC-DCP): A modified version of DCP with reduced contact to the bone to minimize disruption of blood supply.
Design and Configuration:
Bone plates come in various shapes and configurations to accommodate different anatomical sites and fracture patterns.
Anatomically contoured plates are shaped to match the curvature of specific bones, improving the fit and reducing soft tissue irritation.
Hole Patterns:
Bone plates have an array of holes for screws, allowing for flexibility in fixation and promoting optimal bone alignment.
Screw holes may be designed for compression, neutralization, or locking screw placement.
Thickness and Profile:
Plates are available in different thicknesses and profiles to suit the biomechanical demands of specific anatomical locations and patient demographics.
Surface Finishes:
Some bone plates undergo surface treatments or coatings to enhance biocompatibility and promote bone integration.
Sterilization:
Orthopedic bone plates are sterilized before use to maintain aseptic conditions in the surgical environment.
Advantages of Titanium:
Biocompatibility: Titanium’s biocompatibility reduces the risk of inflammation or rejection by the body.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium resists corrosion in biological environments, contributing to long-term stability.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium offers high strength with a relatively low density, making it an ideal material for orthopedic implants.
Indications:
Bone plates are used in various orthopedic procedures, including fracture fixation, corrective osteotomies, and joint fusions.
Radiopacity:
Titanium bone plates are often radiopaque, facilitating their visualization on medical imaging such as X-rays.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.