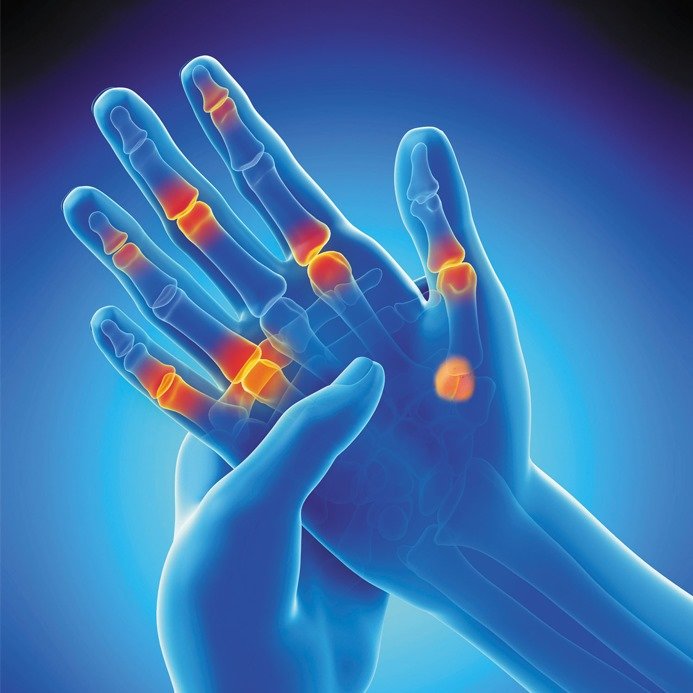
What Is Arthritis?
Types of Arthritis
Symptoms of Arthritis
What Causes Arthritis?
Diagnosis of Arthritis
Treatment of Arthritis
Prevention of Arthritis
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a joint disorder that causes the inflammation of one or more joints leading to pain. It is an umbrella term for over 100 different forms of joint disorder. Each form of arthritis comes with its own set of complications, causes and prognosis. The most common forms of this condition are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis. Other common types include psoriatic arthritis, (associated with conditions), gout (deposition of uric acid), etc. Almost 50 million people around the world are affected by one or another form of arthritis.
Types of Arthritis
Broadly speaking, there are two types of arthritis: Inflammatory and Non-inflammatory.
Non-inflammatory Arthritis
Osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia and back ache are the common forms of non-inflammatory arthritis.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Regardless of the type, arthritis causes pain and limits your range of movement.
The pains last for more than a week
You experience unexplained joint pain usually accompanied with fever
You experience difficulty in carrying out daily chores due to joint pain
Your joint pain isn’t cured by pain killers
There is swelling and stiffness in the joints
What Causes Arthritis?
The trigger behind arthritis varies depending on the form of this condition. Moreover, a combination of factors can be the culprit behind this joint disorder. Here are some of the common factors that contribute to most forms of arthritis. The contributing factors behind arthritis include:
Injury- It may cause degenerative arthritis
Abnormal metabolism-It leads to gout
Genetic predisposition-It increases your risk of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
Infections-such as in the arthritis of Lyme disease
Immune System Dysfunction-It leads to rheumatoid arthritis
Smoking
Obesity-It leads to degeneration of bones
Age-Your risk increases with age
Gender-Women are more vulnerable to arthritis than men.
Professions that demand long hours of sitting.
Diagnosis of Arthritis
The diagnosis will be based on your symptoms and the location of inflammation. The tests include blood examination, and X-ray findings, MRI scan, CT scan, synovial fluid analysis and/or a urine test. You may have to visit your doctor several times before he can rule out other causes and confirm the diagnosis. If not diagnosed and treated early, arthritis can be a debilitating disorder.
Treatment of Arthritis
The type of arthritis decides your treatment options. Curative methods may include medications, physiotherapy, exercise, weight control and orthopaedic bracing. Eroding forms of arthritis may require joint replacement surgery. Medicines are advised to reduce inflammation and pain in the joint. There is no permanent cure for arthritis.
Medications
Doctors generally prescribe pain killers, anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroids. Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are also suggested to suppress underlying inflammatory diseases. Biologic drugs are used in treating rheumatoid arthritis or when DMARDs are ineffective.
Hydrotherapy
It involves special exercises that you do in a warm-water pool.
Physiotherapy
Due to pain, you will often avoid moving the affected joint. A physiotherapist can help you work out the joint stiffness without damaging it.
Occupational therapy
It promotes health and well-being by teaching you how to reduce the strain on your joints during your daily activities. Your home and workplace may be modified by your occupational therapist so that you can move about without worsening your arthritis.
Surgery
It is usually recommended when other treatment options fail and the damage to your joints is severe enough to affect your functionality. Surgery can either be pain-relieving or reconstructive. Surgical interventions include replacing a badly damaged joint with an artificial joint, removing the inflamed lining of the joint cavity, releasing trapped nerves or fusing a joint to make it more stable. The most common form of surgery for arthritis is joint replacement.
Prevention of Arthritis
Some forms of this joint disorder cannot actually be prevented because they are the results of non-modifiable factors like age, genes and gender. However, a few habits may reduce your risk of arthritis:
Maintain a healthy body weight
Your knees bear the most of your weight. So, being overweight will hurt them the most and lead to erosion of the joint. Regular workout is the key to keeping off the extra kilos and strengthen your muscles and joints. Follow a routine that combines aerobic workouts, strength training exercises, and light stretches.
Keep injuries at bay
Degeneration of joints is a natural phenomenon of ageing. But this process becomes faster when your bones are injured and cartilage damaged. To reduce your risk of injury, use adequate safety equipment if you are involved in any kind of sport. Learn the right techniques while exercising.
Pay attention to your posture
The posture that you use while sitting, standing or lifting weights determines the health of your bones and muscles to a large extent. While picking up an object, keep it close to your body and lift your knees and hips instead of your back. This will make sure that your back muscles and wrists are not strained. Also, while sitting for long hours, your back, legs and hands should be supported well.

