Purpose and Function:
The primary purpose of an orthopedic hip prosthesis system is to restore mobility and alleviate pain in individuals with hip joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, fractures, or avascular necrosis.
The system replaces the damaged hip joint with artificial components to restore joint function, stability, and range of motion.
Components of the System:
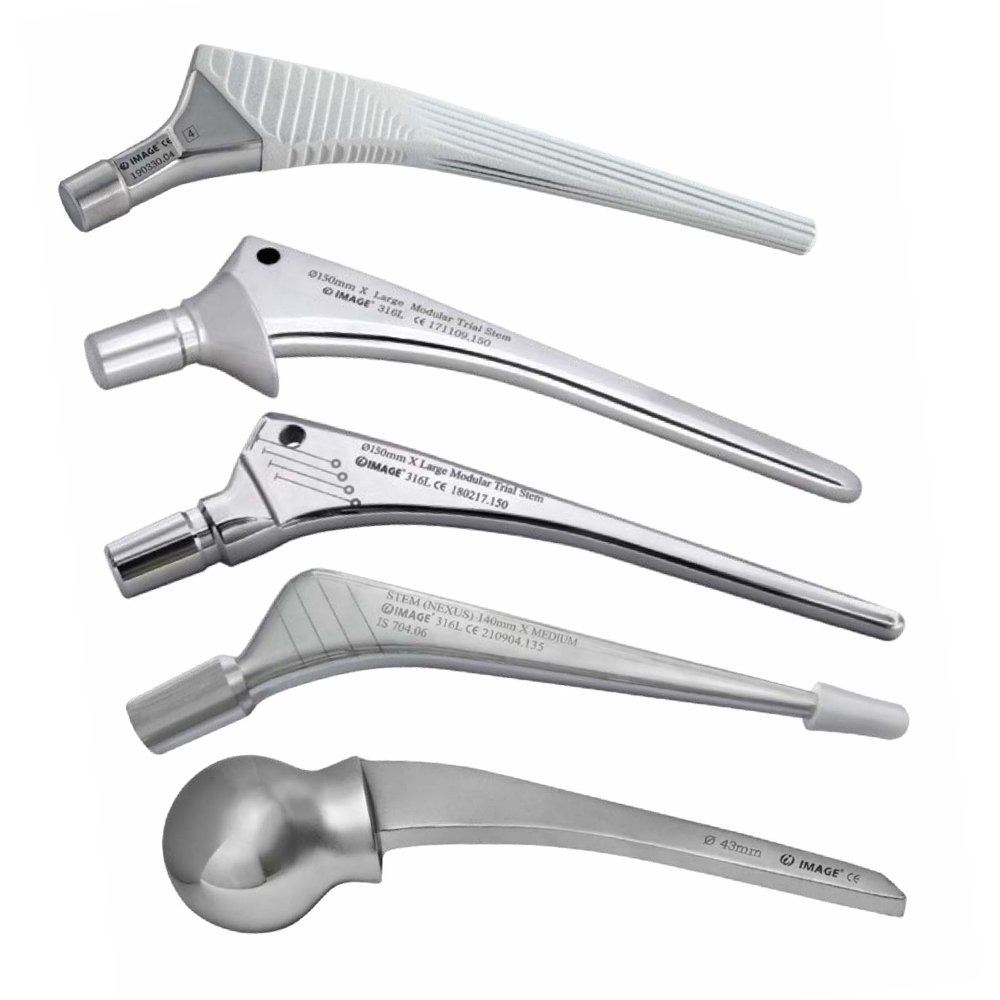
Hip Stem: The stem is a component that is inserted into the femur, serving as an anchor for the prosthesis.
Femoral Head: The femoral head is the ball-shaped component that replaces the natural femoral head and fits into the hip socket.
Acetabular Cup: This cup replaces the damaged hip socket (acetabulum) and is typically made of materials like metal, ceramic, or polyethylene.
Liner: The liner is placed within the acetabular cup and can be made of various materials, such as polyethylene, to reduce friction.
Materials:
Orthopedic hip prostheses are commonly made from biocompatible materials such as titanium, stainless steel, ceramic, and high-density polyethylene. The selection of materials depends on factors such as durability, wear resistance, and biocompatibility.
Biomechanical Considerations:
The design of hip prostheses takes into account the biomechanics of the hip joint to restore natural movement patterns and stability.
The articulating surfaces of the prosthetic components are engineered to minimize wear and optimize longevity.
Surgical Techniques:
Total hip arthroplasty involves precise surgical techniques to remove the damaged joint components and securely implant the prosthetic components.
Surgeons may use minimally invasive approaches to reduce tissue trauma and expedite recovery.
Cemented vs. Uncemented Prostheses:
Some hip prostheses are cemented into place using bone cement, while others rely on the bone’s natural ability to grow and adhere to the prosthesis (uncemented).
Postoperative Care:
Patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty with a hip prosthesis system typically undergo rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility.
Regular follow-up appointments monitor the healing process and assess the functionality of the hip prosthesis.
Patient Considerations:
Patient factors such as age, activity level, bone quality, and overall health influence the choice of hip prosthesis components and surgical approach.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.